Was there always government? It seems safe to think government doesn’t always exist. Early humans wander around in groups. They settle conflicts or issues within the family. That includes the extended family meaning the clan or tribe.
The Agricultural Revolution brings about many changes in the way people live. Most important, people are stationary. They are attached to plots of land essential to growing the food that ensures their survival. This new form of society requires order, structure, and cooperation. The successful agriculture of the river valley civilizations is based on irrigation. Building, operating, maintaining, and expanding the irrigation network appears to require government.
Just how organized government comes into being is open to question. People are people. Some type of social understanding or social dynamic takes place to create the social institution we call organized government.
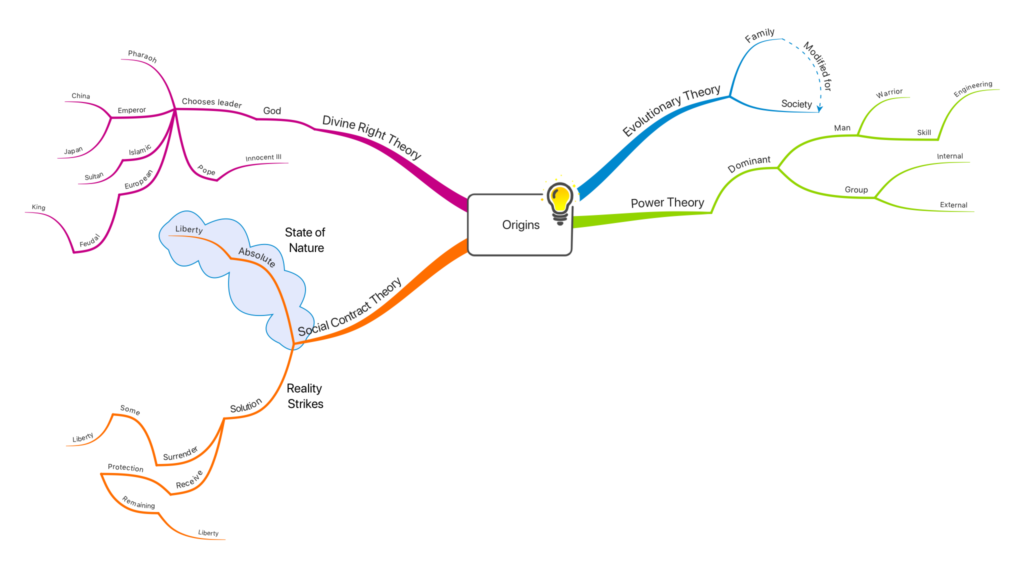
There are four theories of how governments originated.
- Evolutionary Theory
- Power Theory
- Divine Right Theory
- Social Contract Theory
Evolutionary Theory
This theory argues that government evolved from the family. The power and control structures of the family are adapted. In new forms, they become the power and control structures of a larger society. Power and control structures within a family are designed to protect the family unit. They are there to ensure the survival and prosperity of they family members. At some moment in time, it’s argued, some one says, “what if we take the way we run our families and use it to run to greater community”?
Power Theory
The Power Theory argues that one group use force to take control of another group. This theory would argue that those with the specialized knowledge in engineering irrigation networks force the rest of society to be ruled by them. People have no choice but to agree. The people, the farmers, need the irrigation network in order to grow the harvest levels the community needs to live.
The fact that the first Chinese ruler is called the Great Engineer gives some credibility to this idea. Of course, in time, nomadic societies conquer and rule some of the much richer sedentary agricultural societies.
Divine Right Theory
Divine Right Theory argues government came from organized religion. Professional religious leaders argue that they or some one they choose is destined to rule. Ordained by god to govern the people. The ancient Egyptian pharaoh proclaimed himself a god in the making — divine. Ancient Egyptian government is a theocracy, the rule of the Egyptian people by the gods through the god in making, the pharaoh. When Octavian makes himself the ruler of Rome he is granted the title of the Divine Augustus — the god Augustus. European kings ruled by divine right granted them by the Christian God. Islamic rulers, like the Ottoman Sultans, ruled by the will of Allah. The emperor of China rules by the Mandate of Heaven. The emperor of Japan claims to be a direct descendent of the Sun Goddess.
Social Contract Theory
Social Contract Theory argues there is a clearly stated agreement by which the people surrender some of their natural liberty to ensure their remaining liberty on a more permanent and secure basis. No one individual has the ability, the strength across their lifetime, to maintain their absolute liberty. There is some one or some group strong enough to take away one’s absolute liberty. Solution? Give up some of your liberty to a government. Give enough of your liberty that the government gains the power and control needed to protect your remaining liberty.
This theory is an idea of the European Enlightenment. It proposes a rational explanation for the origins of government. It primarily grows out of English political thinking. It reflects the fact that the English feudal monarchs are tightly controlled by what is called the Feudal Contract. The Feudal Contract in England creates the council guiding and controlling the King that becomes Parliament. The English King’s government exists by means of a contract between the people, the nobility, and the Crown.